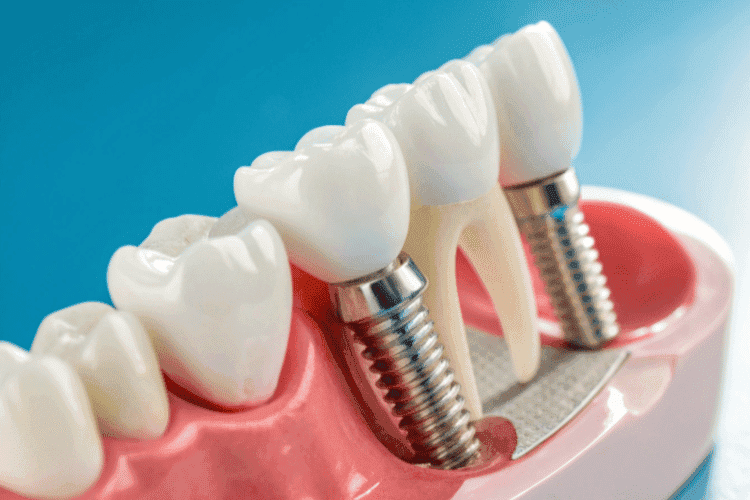
Dentures and Dental Implants
Choosing between dentures and dental implants is a decision that people with missing teeth should make. Each solution comes with advantages and limitations. Also, implants and dentures suit different people depending on factors such as individual dental health and budget.
In this guide, we’ll talk about the differences between the two and help you determine what’s best for your needs.
What are Dentures?
Dentures (also called false teeth) are removable prosthetics for replacing missing teeth. They restore function and appearance, allowing you to speak and eat more comfortably. Traditional dentures are removable and rely on the natural shape of your mouth and suction to stay in place. However, there are snap-in and fixed options that use implants and surgery.
Types of Dentures
Full Dentures
Dentists use complete dentures when all your natural teeth are missing in the upper or lower jaw. The upper jaw gets traditional dentures that use suction to stay in place. The lower jaw dentures are horseshoe-shaped to keep out of the way of your tongue. Your dentist may also use a dental adhesive to help full dentures remain in place.
Partial Dentures
Partial dentures fill the gaps left by a few missing teeth and are held in place with metal clasps. These are ideal for those who still have some remaining teeth. Partial dentures are important because they prevent your natural teeth from shifting into the empty spaces. These dentures can help prevent damage to your bite over time.
Immediate Dentures
Dentists place immediate dentures on the same day they extract your teeth. Immediate dentures act as a healing bandage after tooth loss or extraction. Your gums and bone will shrink as they heal, so you will need realignment or replacement for immediate dentures after about six months.
Implant-Supported Fixed Dentures
This is a hybrid solution where a dentist anchors dentures using dental implants. These offer more stability than removable dentures.
Implant-supported dentures snap onto metal posts (implants) that an oral surgeon places in the jawbone. This design prevents the slipping that happens with lower dentures and allows you to eat tougher foods like steak or apples more easily. Because of these mechanics, you cannot remove them yourself, making them permanent dentures.
3D Printed Dentures
Dental lab technicians custom-make 3D-printed dentures using digital technology, which provides a more precise fit and a quicker turnaround.
Instead of biting into a semi-fluid impression material, the dentist scans your mouth with a digital camera. This creates a digital file, which goes to the dental lab to make the structures. The digital file is often permanent, so if you lose your dentures on vacation, your dentist can print an exact replacement without needing you to go in for new molds.
Pros and Cons of Dentures
 Photo by Truecreatives on Canva
Photo by Truecreatives on Canva
Pros
- Cost-Effective: Traditional dentures are cheaper than dental implants or fixed bridges. They are often the most affordable way to restore a complete smile and oral function on a budget.
- Non-Surgical: Unlike implants, which require drilling into the underlying bone, traditional dentures just need a mold of your mouth. It makes them ideal for people on a smile journey who want to avoid surgery or who have a medical history that makes surgery risky.
- Suitable for Most Patients: Even if you have experienced gum disease or jawbone loss, you can usually still wear a traditional denture.
- Facial Structure Support: Dentures are replacement teeth that fill out your cheeks and lips, helping prevent the sunken look that often happens after tooth extraction.
- Health Safety Net: Dentures help prevent digestive issues by allowing you to chew properly.
- Protection for Remaining Teeth: Partial dentures prevent the adjacent teeth from moving into the gaps, which helps keep your remaining teeth stable and your bite aligned.
- Facial Aesthetics: Dentures can help fix an ‘unattractive smile’ for confidence and self-esteem.
Cons
- Can Become Loose: Without tooth roots, the jaw structure naturally shrinks over time. As the bone moves, the denture that fits perfectly starts to slip.
- May Affect Taste and Feel: Upper dentures cover the roof of your mouth, which contains some taste receptors. This can make food taste different. Also, since the teeth aren’t anchored to your bone, you can’t feel the texture or temperature of food as clearly as you could with natural teeth.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Traditional dentures are fragile and can break if you drop them. You also need to replace them every five to 10 years because they wear down and your mouth shape changes.
- Bone Loss: Traditional dentures sit on top of the gums and don’t stimulate the jawbone. Over time, the body reabsorbs that bone, causing the jaw to shrink.
- Denture Stomatitis: If you do not clean your dentures well or maintain good long-term oral health, the fungus Candida can grow underneath them, causing gum irritation, soreness, itching, and redness.
What are Dental Implants?
Dental implants are titanium posts that a surgeon places into the jawbone to act as artificial tooth roots. Once healed, they support prosthetic teeth, such as crowns (for at least one tooth), bridges (for several missing teeth), or permanent dentures (for an entire arch of teeth).
Dental implants integrate titanium posts because they are biocompatible, allowing a process called osseointegration. This is when the jawbone grows and attaches to the post, making it a permanent part of the bone structure. This healing period is usually three to six months. Dental implants are a permanent option for replacing one or more teeth.
Types of Dental Implants
Endosteal Implants
The most common type, which dentists place directly into the jawbone. Endosteal implants look like small screws, and thanks to modern technology, they require small incisions and have faster healing times.
Subperiosteal Implants
Oral surgeons place these under the gum but above the jawbone. Subperiosteal implants are ideal for patients with a lot of bone loss, much more than for standard implants. They help patients avoid bone grafting surgery.
Zygomatic Implants
Surgeons anchor these implants in the cheekbone. Zygomatic implants are extra-long and an option for upper-jaw implants in patients with severe bone loss.
All-on-4/All-on-6 (Full Arch)
All-on-4 implants or all-on-6 implants support a full arch of teeth with just four or six implants. They are a permanent, non-removable set. Oral surgeons use the densest parts of your remaining bone to support a full bridge of 10–14 teeth.
All-on-4 and All-on-6 implants are the best option for long-term denture wearers because they offer improved stability, support bone growth, and look like real teeth for a beautiful smile. If you’re missing all the teeth on your upper or lower arch, this is the best solution.
Mini Dental Implants (MDIs)
MDIs are smaller in diameter, and surgeons often use them to stabilize removable implant-supported dentures. They are less invasive and cheaper than full-sized implants. However, MDIs are not as strong, so oral experts rarely use them for molars.
Ceramic (Zirconia) Implants
These implants are metal-free, making them ideal for patients with metal sensitivities. Also, because they are white, people choose them for front teeth so that they blend with the surrounding teeth.
Pros and Cons of Dental Implants
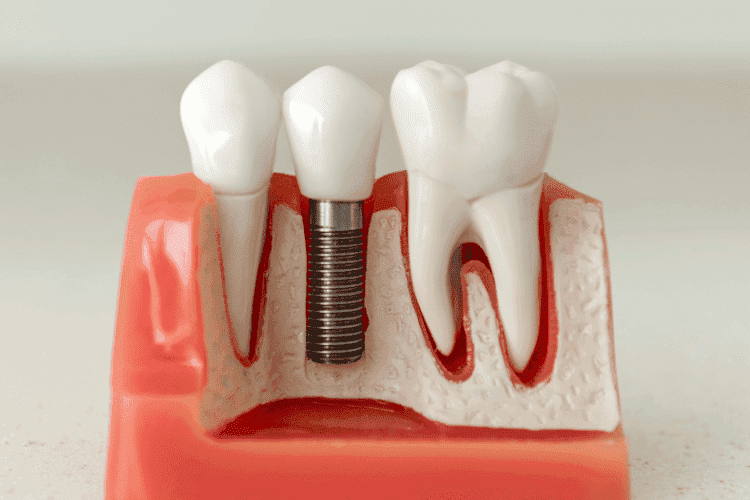 Photo by turk_stock on Canva
Photo by turk_stock on Canva
Pros
- Long-Lasting: Because the titanium post fuses with your living bone, it becomes a permanent part of your body. A properly maintained dental implant can last 25 years or a lifetime.
- Prevent Bone Loss: Your jawbone needs the exercise of chewing to stay healthy. Dental implants act like artificial roots, sending signals to the bone to stay strong.
- Feel and Function Like Natural Teeth: Dental implants don’t slip like dentures. You get back almost 100% of your natural biting force, so you can eat just as you did with your existing teeth.
- Easy Cleaning: You can brush and floss a dental implant just like a real tooth.
Protection of Adjacent Teeth: Dental implants stand on their own, protecting the surrounding teeth.
Cons
- Higher Initial Cost: A single implant can cost over $3,000, making replacing missing teeth more expensive.
- Oral Surgery and Healing Time: You must have dental implant surgery to place the post. After your surgeon places the implant, you have to wait three to six months for the bone to grow around the post.
- Not Suitable for All: If you have been missing teeth for a long time, your jawbone may have already thinned too much to hold an implant. Also, conditions such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders can increase the risk of the implant failing to fuse with the bone.
Differences Between Dentures and Dental Implants
| Feature | Dentures | Dental Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Stability | Can become loose | Fixed in place |
| Bone Preservation | Does not prevent bone loss | Helps preserve bone density |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and possible replacement | Requires proper care, less frequent replacement |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher upfront cost |
| Procedure | Usually non-invasive | Requires surgery for implant placement and healing |
| Appearance | May appear less natural | Mimics natural teeth |
Paramount Dental: Dentures and Dental Implants Experts
We offer multiple tooth replacement options, including conventional dentures and fixed implant-supported dentures. With our restoration dentistry services, you can even get full mouth dental implants. We also offer multiple sedation dentistry options if you require oral surgery.
Our team at Paramount Dental creates a customized treatment plan based on personal preferences and oral health needs. Trust us to take care of you from the initial visit to healing.
FAQs
Which is Better, Dental Implants or Dentures?
It depends on your needs and preferences. If you’re looking for a more permanent, stable solution and are a good candidate for surgery, implants are the best choice. On the other hand, dentures may be better for people who want a non-surgical and budget-friendly option.
How Long Do You Go Without Teeth When Getting Implants?
You don’t have to go without teeth. While waiting for implants, dentists provide temporary solutions such as partial dentures or bridges for appearance and function.
How Much Do Dental Implants Cost?
Dental implants can range from $3,000 to $5,000 per implant. The exact number often depends on the facility you choose.
Can You Get Dental Implants if You’ve Had Dentures?
Yes, many patients transition from traditional dentures to implants. However, your oral surgeon will check your bone density and oral health before putting in implants.
Can Dentures be Put in Permanently?
Yes. Permanent dentures, supported by implants, are a fixed option compared to removable dentures.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between dentures and implants is a personal decision that depends on factors such as cost, comfort, lifestyle, and oral health. Always consult qualified experts to guide you to the best choice for your smile.